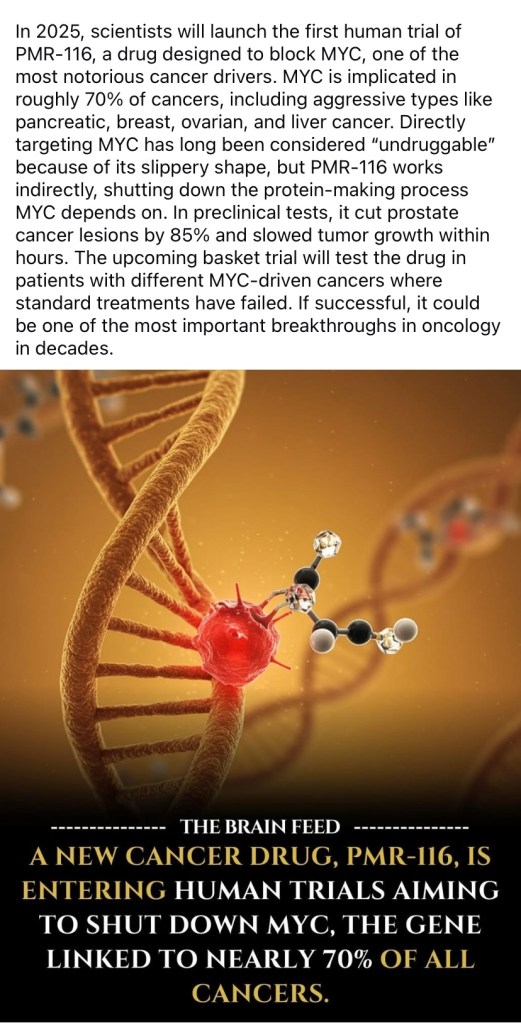
A revolutionary cancer vaccine has shown astonishing success in clinical trials, targeting pancreatic and colorectal cancers—two of the most lethal and treatment-resistant forms. Developed by BioNTech and Genentech, the mRNA-based vaccine trains the body’s immune system to recognize and destroy cancer cells with remarkable precision.
In a Phase I trial, 84% of patients showed strong immune responses, and many have remained cancer-free for over 2 years post-treatment. The vaccine customizes its RNA code based on each patient’s tumor, marking a major step toward personalized oncology.
This breakthrough not only provides new hope for terminal cancer patients but also confirms the broader application of mRNA vaccine platforms beyond COVID-19. Experts believe this approach could soon extend to lung, liver, and even brain cancers.